Ever wondered how to differentiate male from female tortoise ? Look no further! This guide will unveil the key physical features that hold the secrets to your tortoise’s gender” Sexing your tortoise is no small feat, yet it’s a critical element of responsible ownership. The ability to discern “male vs female tortoise” not only satisfies curiosity but also plays a pivotal role in tailoring their care, particularly during breeding seasons.
Key Features for Sexing Tortoises
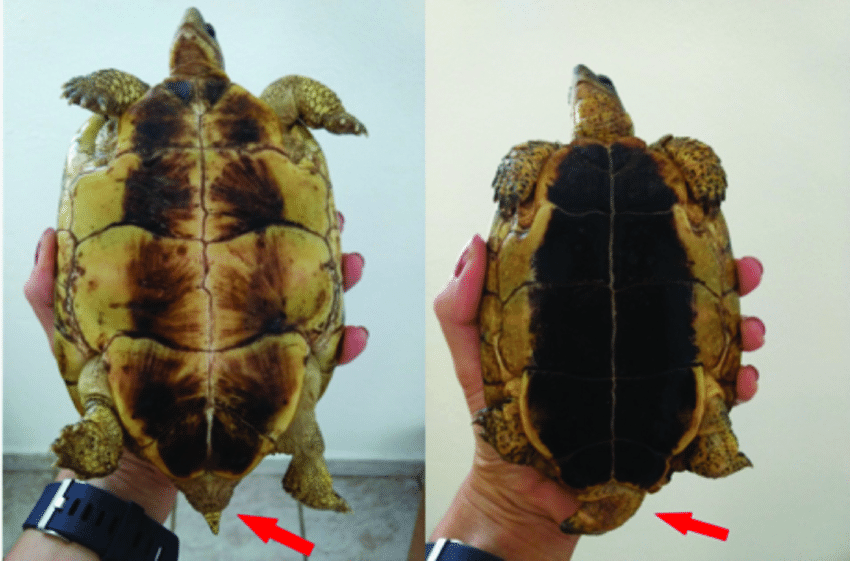
1. Plastron (Underbelly Shell):
In the realm of tortoise gender identification, the plastron takes centre stage. Recognizing a concave plastron as a male characteristic ensures stability during mating, while a flat or convex plastron, often seen in females, provides a secure space for “tortoise sexing.” Clear visual aids accompany these explanations for enhanced comprehension.
1.1 How to sex a tortoise by shell
1.1.a. Pick up the Tortoise:
- Hold the tortoise carefully with both hands, avoiding dropping it.
- Raise the tortoise high enough to see underneath but avoid flipping it on its back as it causes stress.
1.1.b. Inspect the Lower Shell (Plastron):
- The lower shell of the tortoise is called the plastron and is a key indicator of its sex.
- If the plastron is indented or concave, it’s likely a male (helps in mating).
- If the plastron is flat or convex, it’s likely a female (supports egg-carrying).
1.1.c. Confirm the Plastron Shape by Touch:
- Feeling the underside of the tortoise can help determine if the plastron is convex, flat, or concave.
1.1.d. Examine the Anal Scute (Tail End of the Plastron):
- Look at the anal scute for a “V” or “U” shape just beneath the tail.
- A wider, more open angle indicates a male, facilitating tail movement.
- A tighter angle with points close to the marginals suggests a female for added protection.
1.1.d. Return the Tortoise:
- Put the tortoise back down promptly to reduce stress, returning it to its usual environment.
1.1.e. Consider Coloration and Size:
- Males might have brighter coloration, especially during mating, but this method varies among species.
- Note that males are generally smaller than females, with exceptions like red-footed tortoises where both sexes are similar in size.
1.1.f. Examine the Carapace (Upper Shell) for Specific Species:
- For some species, the shape of the carapace reveals the sex.
- Male hinge-back tortoises have elongated bodies, while females are rounder.
- Male Hermann’s tortoises are slightly wider at the rear compared to females of the same species.
Finding the Perfect Companion: Your Comprehensive Guide to “Tortoise for Sale Near Me”
2. Tail Length and Shape:
Delving into subtleties, the tail emerges as a distinctive feature in “sexing tortoise.” Males exhibit longer tails, aiding in copulation, whereas females showcase shorter tails crucial for efficient egg-laying. Visual references capturing these nuances provide a comprehensive understanding of “male vs female tortoise.”
2.1 How to Differentiate Male and Female Tortoise by Tail Length and Shape:
2.1.a.Observe the Tail Without Picking Up the Tortoise:
- Look at the tortoise’s tail without lifting it, especially if it’s shy or in a new environment.
- If needed, crouch down to the tortoise’s level instead of picking it up.
2.1.b. Check the Tail’s Length:
- Assess the length of the tortoise’s tail, as this method is useful for tortoises that cannot be picked up.
- Generally, males have longer tails than females.
- A male’s tail may move from side to side.
- A female’s tail is usually shorter, about the length of a cotton swab’s end.
- A male’s tail is longer but not excessively huge.
2.1.c.Use Photos for Comparison:
- If you’re unsure about tail length, compare the tortoise’s tail to pictures of male and female tortoises.
- Look for images specific to the tortoise’s species for more accurate comparisons.
By following these simple steps, you can determine the sex of a tortoise by observing its tail without causing stress or discomfort.
3. Anal Scute (Tail Opening):
The anal scute, a discreet yet revealing feature, contributes to “tortoise sexing.” Males display a V-shaped configuration, aligned with their reproductive needs, while females sport a U-shaped structure, accommodating their unique role in the reproductive process. Visual representations of these subtle but vital distinctions enhance clarity in “how to differentiate male and female tortoise.”
Additional Considerations
4. Size Differences (Species Specific):
Acknowledging potential size variations is essential in the context of “male vs female tortoise.” Some tortoise species witness females surpassing males in size. However, it’s crucial to emphasize that this size discrepancy isn’t universally applicable and should be considered alongside other characteristics specific to the tortoise breed.
5. Age Limitations:
Patience is key when “sexing tortoise,” especially young ones. Sexing becomes more accurate as tortoises mature into adulthood, overcoming the challenges associated with underdeveloped physical characteristics during their early stages.
6. Professional Help (When to Call a Vet)
In the pursuit of gender clarity, it’s prudent to seek professional guidance. Consulting a veterinarian or an experienced breeder becomes imperative when uncertainties persist in “how to differentiate male and female tortoise.” This is particularly crucial when dealing with tortoises in their early stages or when health concerns arise during the examination process.
V. Conclusion
As we unravel the intricacies of “tortoise sexing,” understanding their unique features becomes paramount. The plastron, tail, and anal scute collectively narrate the story of their gender identity. This knowledge not only satisfies curiosity but significantly contributes to the well-being of tortoises during various life stages.
